Arthritis is a medical condition that causes pain throughout the body and impairs the joints. It develops as a result of a malfunction of the immune system, so it is classified as an autoimmune disease. The immune system works by fighting off things that may be damaging to our bodies, like an infection. But, for people with rheumatoid arthritis, instead of their immune system fighting off infection, it attacks healthy cells, like the tissue that makes up the joints.
Certain people may be at a higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Some of the things that place people at higher risk for developing this disease include:
Sex – women are at an increased chance of developing rheumatoid arthritis compared to men
Age – older individuals have a higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis than younger people
Genetics – people who have a family history of rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop this condition in their own lives
Obesity – people who are overweight are more likely to develop arthritis conditions, specifically rheumatoid arthritis.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. But, it’s clear that rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that is a result of an autoimmune malfunction. So, a person who has rheumatoid arthritis has an immune system that is directly attacking healthy cells that surround joints, making the motion and function difficult with these joints. Furthermore, as rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that impairs healthy cells, not only are joints affected, but other things can also be attacked in a person’s body that lead to symptoms that affect a person’s skin, nerves, lungs, heart, and more.
While the causes of rheumatoid arthritis are not exact, specialists know that genetic factors play a part in its development. This can include genetic predisposition with it being passed down from family members. And, it can also include genetic responses to specific things like illnesses resulting from bacterial or viral infections.
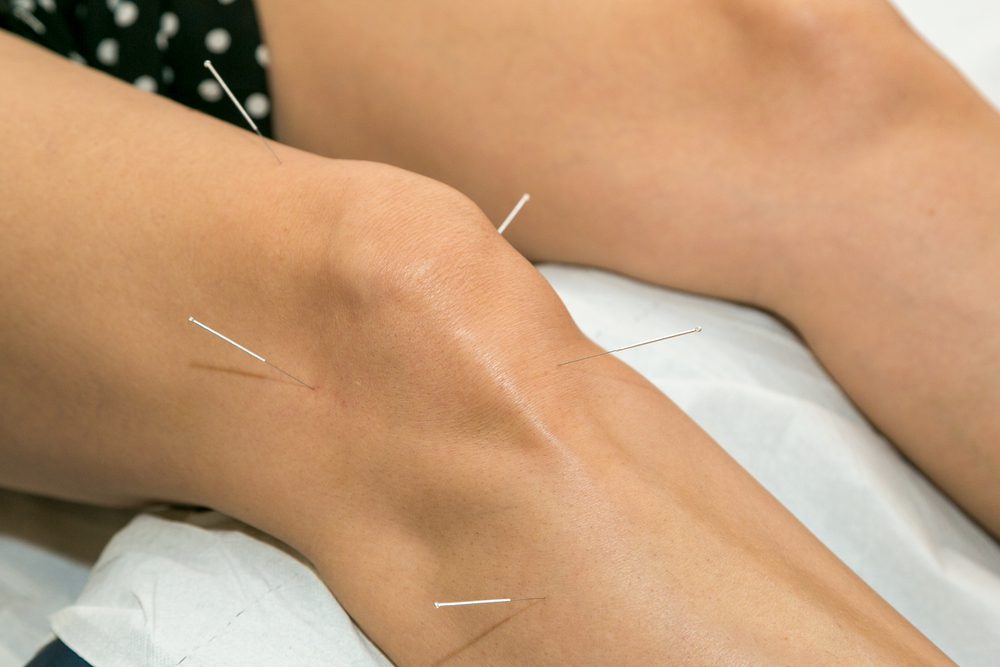
Acupuncture isn’t a cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but it is an effective tool in the treatment of symptom flare-ups and managing symptoms on a regular basis. It’s believed that acupuncture helps to reduce the severity and frequency of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms as it is effective in reducing inflammation, which is the cause of rheumatoid arthritis pain. Choosing acupuncture as a symptom management tool for rheumatoid arthritis may be a good option for people diagnosed with this condition who don’t want to use medications that cause unwanted side effects or experience invasive procedures.
If you’re struggling with the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and are considering acupuncture as a pain management tool, consider the acupuncture sessions at Acupuncture Zen located in Delray Beach. Dr. Tony has many years of experience helping people diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis find the symptom relief they are looking for using acupuncture techniques. Find out more about our holistic acupuncture experience and location today.
The most common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis is pain surrounding the joints. Other symptoms of the medical condition can include:
Some people who are diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis may only experience arthritis symptoms during what are known as “flare-ups”, which are episodes in which symptoms may worsen.