OBJECTIVE:
To study the effectiveness of Electroacupuncture for back pain of the spinal nerve root using a selective spinal nerve block technique for the treatment of lumbar and lower limb symptoms in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis.
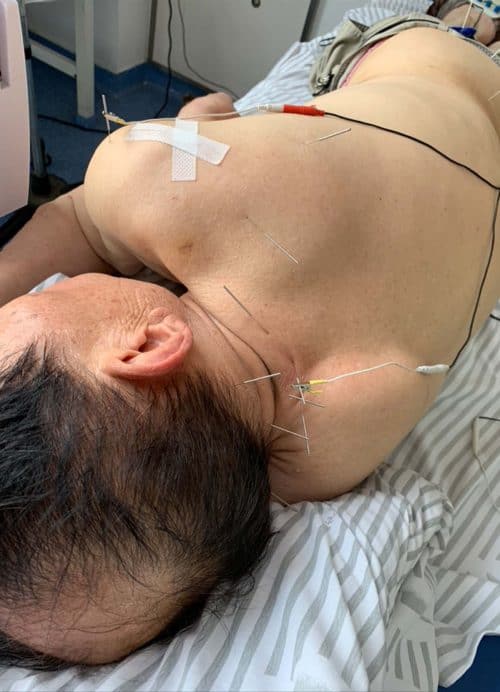
A patient receiving electroacupuncture
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is another condition that sees the benefit of using electroacupuncture.
METHODS:
Researchers studied 17 patients with spinal canal stenosis unresponsive to two months of conservative treatment and conventional acupuncture. Using x-ray fluoroscopy, they inserted two acupuncture needles near the relevant nerve root, guided by symptoms, x-ray, and MRI findings. They applied low-frequency electroacupuncture stimulation (10 Hz, 10 minutes). Patients underwent 3–5 weekly treatments. Evaluators assessed outcomes before and after each session and three months post-treatment.
RESULTS:
After the first nerve root electroacupuncture stimulation, scores for lumbar and lower limb symptoms improved significantly (low back pain, p
CONCLUSION:
Electroacupuncture to the spinal nerve root significantly improved lumbar and lower limb symptoms. Conventional acupuncture and conservative treatments previously failed. Symptoms showed sustained improvement three months post-treatment. Mechanisms likely activate the pain inhibition system. Additionally, nerve blood flow improves.Dr. Tony Willcox actively gained extensive clinical experience in China. He treated numerous patients with varied conditions. Specifically, he utilized electroacupuncture for back pain. Training in Shanghai and Anhui, Dr. Tony mastered acupuncture techniques. He observed its application in hospitals and private practice.
Click Here To View More Articles | Research | Resources
Resources:
– SOURCE: Department of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Meiji University of Integrative Medicine, Kyoto, Japan.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22534725
